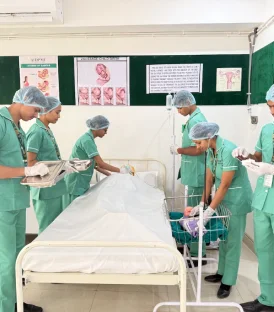
It is a radiographic examination of Hepatic veins in which contrast is injected into the IVC via femoral vein to visualize the abnormalities of the hepatic veins.
Indications
- Obstruction in hepatic veins
- To detects the abnormalities in Hepatic vein
- To evaluate the patency of hepatic vein
- Formation of a blood clot within the hepatic veins
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to contrast
- Blood clotting disorder
- Suspected pregnancy
- Impaired renal function
- Severe phlebitis
- Severe hepatic dysfunction
Equipment
- Fluoroscopy unit with tilting table
- Catheter 5F
- Automatic pressure injector
- Contrast
- Normal Saline
- Antiseptic solution
- Femoral vein access needle
- Guidewire
- Sheath
- Gauze
Patient preparation
- The patient should not eat or drink after midnight.
- Patient KFT reports must be reviewed prior to the examination.
- Ask patient to stop taking anticoagulant before the exam.
- Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Ask the patient to remove clothing and wear hospital gown.
Procedure
- Place the patient in supine position on fluoroscopy table.
- An intravenous line is inserted into the patient arm and sedative medication is given through line to make patient relax.
- The groin area of the patient must be cleaned with the antiseptic.
- The local anaesthesia is given at the insertion site of the groin.
- After numbing the groin area , a vascular access needle is inserted into the femoral vein by using the seldinger technique.
- When the blood comes out from the needle a flexible guidewire is inserted through the needle. After placing the guidewire the needle is removed then the sheath is placed over the guidewire under the fluoroscopic guidance.
- The catheter with side holes is inserted into the femoral vein through the sheath.
- The catheter is smoothly advance through the femoral vein and position inside the iliac vein under the fluoroscopic guidance.
- The contrast media is injected at the rate of 20ml per second for a total of 40ml into the vein through the catheter.
- Ask the patient to perform valsalva maneuver for prolonging filling of contrast media in inferior vena cava then the rapid films are taken at the rate of 1 film per second of the abdomen region in AP, oblique positions.
- After completion of examination the catheter and the sheath is removed and the dressing is applied on the puncture site of the foot.
Aftercare
- Keep the patient under observation BP, heart rate , injected sites swelling and other vital sign should be the monitored.
- Plenty of liquid diet is given to the patient to flush out the contrast media from the body.
Interpretation
- If the venogram shows blood clots or blockage in the veins, the special medicine may be given to dissolve the clot or the ballon angioplasty may be performed.
- To widen the vessels and improve blood flow during the angioplasty a metal stent may be placed by the surgeons.
Submitted by-
Divya Jha